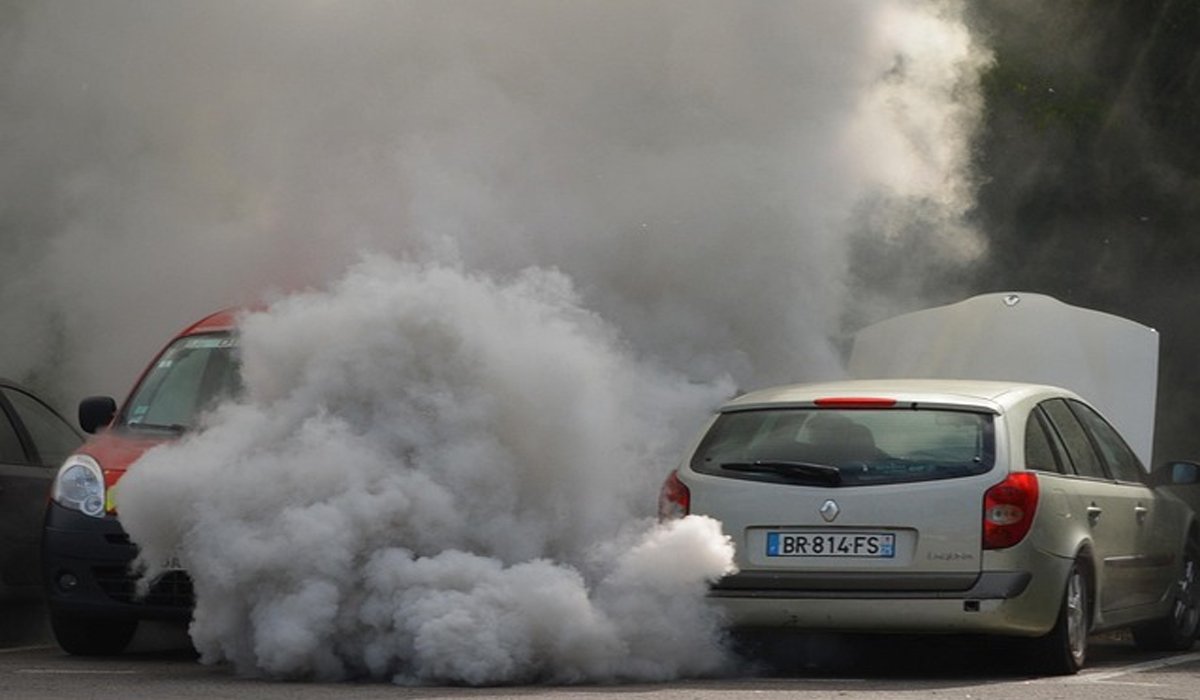
Car exhaust emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution and environmental degradation. Every year, billions of tons of pollutants are released into the atmosphere through motor vehicle use. These pollutants not only harm ecosystems but also pose serious health risks to humans. To combat these adverse effects, it’s crucial to understand the impact of car exhaust and explore ways to reduce it. This article dives into the environmental damage caused by car emissions and highlights potential solutions.
The Composition of Car Exhaust
Car exhaust is a mixture of gases and particles that vehicles emit during engine operation. Common components include:
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas that can replace oxygen in the bloodstream, posing a threat to human health.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): This group of gases contributes to acid rain and smog, harming both vegetation and water ecosystems.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): A greenhouse gas that significantly contributes to climate change by trapping heat in the atmosphere.
- Particulate Matter (PM): Tiny particles that can penetrate the lungs and lead to respiratory issues.
Each of these emissions plays a role in both immediate health problems and long-term environmental damage, making mitigation efforts imperative.
Environmental Impact of Car Exhaust
Vehicles serve as lifelines of modern society, but their emissions come with steep ecological costs. These include:
1. Air Pollution
Car exhaust is a major source of urban air pollution. Cities with high traffic volumes often experience smog, a thick haze that reduces visibility and affects air quality. Smog primarily results from the interaction of NOx emissions with sunlight, creating ground-level ozone, which is harmful to both human health and the environment.
2. Climate Change
The combustion of fossil fuels releases CO2, one of the primary greenhouse gases responsible for global warming. Transportation alone accounts for approximately 24% of global CO2 emissions. Increasing temperatures drive severe weather events, damage ecosystems, and disrupt agricultural patterns globally.
3. Soil and Water Contamination
When exhaust particles settle on the ground, they can seep into the soil and water supply. Acid rain, a byproduct of NOx emissions, acidifies water bodies, killing aquatic plants and animals. Similarly, the presence of heavy metals in vehicle emissions can poison soil, rendering it infertile.
4. Ecosystem Disruption
Pollutants from car exhaust affect more than just the air and soil – they can disrupt entire ecosystems. Acid rain reduces biodiversity in freshwater and forests, while ground-level ozone diminishes crop quality and plant health.
Reducing Car Exhaust Pollution
Addressing car exhaust involves individual actions and systemic changes. Below are practical steps and strategies to reduce emissions:
1. Adoption of Cleaner Fuel Alternatives
Switching to fuels with fewer carbon emissions, such as natural gas or biofuel, minimizes a car’s environmental footprint. Additionally, electric vehicles (EVs) offer a promising solution by eliminating tailpipe emissions.
2. Routine Vehicle Maintenance
Regular vehicle checks and proper maintenance can significantly decrease pollutants. Ensuring that engines operate efficiently, replacing old filters, and keeping tires properly inflated can all reduce the volume of harmful emissions. For instance, staying up-to-date with an emissions test in Provo ensures vehicles comply with regulatory emission standards while operating optimally.
3. Promotion of Public Transportation
Reducing the number of vehicles on the road can immediately cut overall emissions. Cities that invest in frequent, reliable public transport encourage alternatives to individual car use and, in turn, improve air quality.
4. Urban Planning and Policies
Governments can take proactive steps by implementing policies such as congestion charges, low-emission zones, and incentives for purchasing EVs. Urban planning that prioritizes pedestrian and cycling infrastructure also reduces dependence on cars.
Technology and Innovations in Reducing Car Exhaust
Automotive technology continues to evolve to mitigate emissions:
- Catalytic Converters: These devices transform harmful gases like carbon monoxide into less hazardous emissions before they leave the car.
- Hybrid and Electric Vehicles: Hybrids reduce fuel consumption by incorporating battery-powered systems, while electric cars eliminate tailpipe pollutants.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency Standards: Advances in engine technology aim to reduce the amount of fuel burned, lowering emissions per mile traveled.
Manufacturers are also exploring the feasibility of hydrogen fuel cells and renewable energy sources to further revolutionize transportation.
The Role of Global Collaboration
Fighting pollution demands collective global action. International agreements, such as the Paris Climate Accord, emphasize reducing greenhouse gas emissions from all sectors, including transportation. Countries must work together to set and meet aggressive goals for clean energy adoption and vehicle electrification.
Moving Toward a Greener Future
While car exhaust remains an ongoing challenge, progress is achievable through education, innovation, and policy reform. Small changes in individual habits, such as carpooling or using alternative transportation, can add up over time. Coupled with government regulations and advancements in technology, these efforts pave the way for cleaner air, healthier ecosystems, and reduced climate impact.
By addressing car exhaust emissions with urgency and intentionality, we can make strides in reducing pollution and protecting our planet for generations to come.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: Why Your Car Roof Might Be Letting in Water